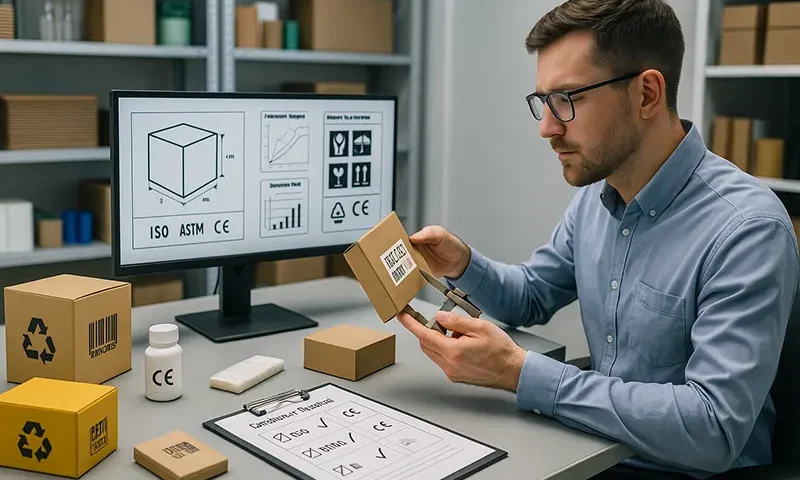
Packaging plays a crucial role in modern commerce, ensuring products are protected, transported safely, and presented professionally. However, behind every box, bottle, and wrapper lies a complex framework of rules designed to safeguard consumers, support environmental goals, and maintain a fair marketplace. Businesses of all sizes must understand these regulations to avoid penalties, maintain customer trust, and keep operations running smoothly.
Why Packaging Rules Matter
Packaging standards exist to manage everything from material usage and labelling to recyclability and waste reduction. Governments and regulatory bodies implement these rules to tackle issues such as excessive waste, misleading branding, and hazardous materials. For businesses, staying compliant is not just about avoiding fines; it’s about demonstrating responsibility and commitment to sustainability.
Companies that stay ahead of regulatory shifts often benefit from improved brand reputation and smoother supply chain management. By adopting high-quality materials, clear labels, and environmentally friendly designs, they meet both regulatory expectations and consumer preferences.
Key Principles Behind Packaging Regulations
Product Protection and Safety
The primary purpose of packaging is to protect the product. Regulations may specify minimum durability standards, tamper-evident features, or suitability for specific types of goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, or cosmetics. Safe packaging helps prevent contamination, damage, and spoilage, which reduces waste and improves customer satisfaction.
Accurate Labelling
Clear and truthful labelling is legally required across many sectors. Labels must often include product details, ingredients, usage instructions, warnings, and recycling information. Misleading or incomplete labels can result in recalls and reputational damage.
Environmental Responsibility
Sustainability is now a major focus of packaging rules. Many countries are reducing the use of single-use plastics, setting recycling targets, and encouraging packaging designs that minimise environmental impact. Businesses may also be expected to report material usage and demonstrate reductions over time.
Types of Packaging Regulations Businesses Should Know
Material Restrictions
Some materials may be banned or limited due to their impact on health or the environment. Companies need to track which substances are permitted and ensure their suppliers comply.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
EPR schemes place responsibility for packaging waste on the businesses that produce or sell packaged goods. This may involve fees, recycling obligations, or mandatory reporting. As global sustainability policies evolve, EPR requirements are becoming more demanding.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Sectors like food and drink, healthcare, and chemicals face additional rules. Temperature sensitivity, hygiene standards, and chemical safety all shape packaging choices in these industries.
The Growing Importance of Sustainable Packaging
Consumers increasingly favour brands with eco-friendly values, and governments are responding with tighter regulations. Businesses must consider renewable materials, efficient production methods, and the full life cycle of their packaging.
Adopting sustainable solutions can also help reduce costs in the long run. Lightweight materials, smart design adjustments, and improved transport efficiency can all contribute to savings.
Ensuring Compliance Across the Supply Chain
Compliance is not just the responsibility of one department; it involves collaboration across procurement, design, manufacturing, logistics, and legal teams. Regular audits, robust documentation, and clear communication with suppliers are essential.
Technology is also playing a bigger role. Digital reporting systems, traceable materials, and automated checks help companies stay compliant and adapt quickly to new regulations.
Navigating the Complex Landscape of Regulatory Change
The rules surrounding packaging continue to evolve, particularly as environmental priorities shift. Businesses must keep informed through industry bodies, regulatory updates, and professional guidance.
This is where understanding tools and frameworks such as packaging compliance becomes increasingly important. Companies that monitor updates proactively avoid last-minute changes and costly disruptions. Building internal knowledge and training teams on regulatory expectations is essential for long-term stability.
Many organisations also turn to professional consultants or specialist platforms to help them manage ongoing obligations. These resources can simplify reporting, track material usage, and ensure that all products meet legal requirements across different markets. Embracing structured approaches to packaging compliance not only reduces risk but also supports a more sustainable and efficient business model.
Final Thoughts
Packaging regulations continue to shape how businesses operate, influencing design, materials, labelling, and sustainability efforts. With consumer expectations evolving and environmental pressures rising, companies must take a proactive approach to managing their responsibilities. By understanding the key principles, keeping informed of regulatory changes, and embedding compliance into everyday processes, organisations can protect their brand, support the planet, and deliver reliable products to customers.