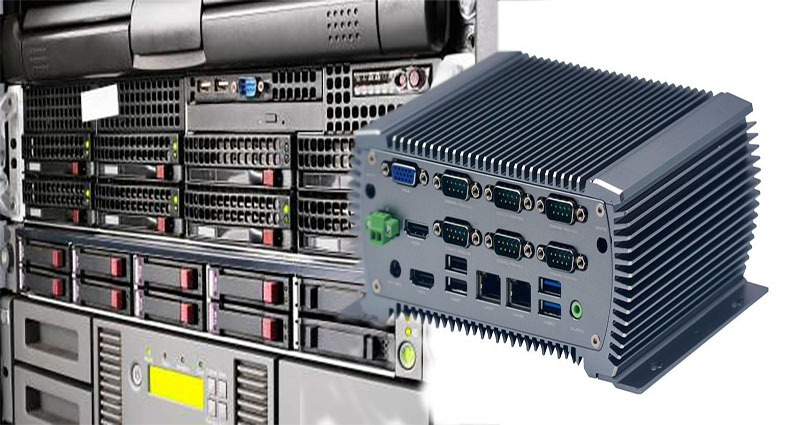
What Is Industrial PC?
Industrial PCs are the most effective way to stay on top of the competition and keep up with new technology. The Information Technology departments of companies are responsible for physical implementation, software installation, and PC configuration. Substandard PCs and IT infrastructure can impact overall performance and customer service. Industrial PCs are an ideal solution for such businesses that may not be able to afford a standard PC. There are several reasons to consider an Industrial PC for your business.
Embedded computer systems
An embedded computer system is a small, non-portable computing device that performs a particular task without any external hardware. The systems can be made of a single-board computer, microcontroller, or Internet of Things (IoT) gateway. They can monitor data remotely or control machinery manually. The embedded computer system can also be used to store data or handle environmental conditions. To further optimize their use, embedded computer systems are … Continue reading >>>