Types Of Backbone Networks
 A backbone is the portion of the computer network infrastructure that interconnects unique networks and provides a path for exchange of data in between these different networks. Backbone networks may well themselves be multilevel, incorporating low-capacity terrestrial links, higher-capacity terrestrial links, and satellite links. This ring could represent the minimum cost of WAN circuits, compromised by an initial estimate of big site visitors flows, and possibly some extremely certain delay requirements (though this is uncommon, with notable exceptions getting higher-overall performance networks). Even though there are an infinite quantity of techniques in which network designers can build backbone networks, there are genuinely only 3 fundamental architectures that can be combined in diverse methods.
A backbone is the portion of the computer network infrastructure that interconnects unique networks and provides a path for exchange of data in between these different networks. Backbone networks may well themselves be multilevel, incorporating low-capacity terrestrial links, higher-capacity terrestrial links, and satellite links. This ring could represent the minimum cost of WAN circuits, compromised by an initial estimate of big site visitors flows, and possibly some extremely certain delay requirements (though this is uncommon, with notable exceptions getting higher-overall performance networks). Even though there are an infinite quantity of techniques in which network designers can build backbone networks, there are genuinely only 3 fundamental architectures that can be combined in diverse methods.
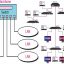
There is a switch serving every LAN (access layer) which is connected to the backbone switch at the bottom of the figure (distribution layer). For the reason that you have a simple want for resilience in the … Continue reading >>>

 A collapsed backbone (inverted backbone, backbone-in-a-box) is a form of backbone network architecture. This sort of network can have daisy chain linked devices for the backbone, nonetheless, designer really should think about the same limitations as for the serial backbone. It is as fast as a bridge for similar information link sort networks, but can also connect distinctive data hyperlink variety networks. The idea behind switched ethernet – and all switched media technologies – is straightforward replace the LAN hub with a switch.
A collapsed backbone (inverted backbone, backbone-in-a-box) is a form of backbone network architecture. This sort of network can have daisy chain linked devices for the backbone, nonetheless, designer really should think about the same limitations as for the serial backbone. It is as fast as a bridge for similar information link sort networks, but can also connect distinctive data hyperlink variety networks. The idea behind switched ethernet – and all switched media technologies – is straightforward replace the LAN hub with a switch. A backbone network is the focal point exactly where all the visitors carried in the access networks converges to be switched and routed to the appropriate destination. Packet switching may be used internally by backbone networks to take benefit of these site visitors patterns, even although the backbone network might present a circuit-switching look to external hosts (see virtual circuit ). Visitors-pattern evaluation could be applied to construct backbone networks that decrease certain network parameters, such as average delay, circuit costs, and so forth.
A backbone network is the focal point exactly where all the visitors carried in the access networks converges to be switched and routed to the appropriate destination. Packet switching may be used internally by backbone networks to take benefit of these site visitors patterns, even although the backbone network might present a circuit-switching look to external hosts (see virtual circuit ). Visitors-pattern evaluation could be applied to construct backbone networks that decrease certain network parameters, such as average delay, circuit costs, and so forth.