Backbone Core Network Design Cisco Network Topology And Style
 Is a generally applied application that uses a net browser and flash to test the connection speed from a device to a selected point on the World wide web. In the above image, accomplished by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson of the NCSA, is a visual representation of what an Internet backbone in the United States. Most organizations now use switched backbones in which all network devices for a single element of the building are physically positioned in the similar space, typically in a rack of equipment. Routers connect two or much more LANs that use the same or distinct information link protocols, but the same network protocol. The purpose of the backbone is to connect regional distribution networks and, in some instances, to offer connectivity to other peer networks.
Is a generally applied application that uses a net browser and flash to test the connection speed from a device to a selected point on the World wide web. In the above image, accomplished by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson of the NCSA, is a visual representation of what an Internet backbone in the United States. Most organizations now use switched backbones in which all network devices for a single element of the building are physically positioned in the similar space, typically in a rack of equipment. Routers connect two or much more LANs that use the same or distinct information link protocols, but the same network protocol. The purpose of the backbone is to connect regional distribution networks and, in some instances, to offer connectivity to other peer networks.
If a network backbone goes down your Web connection speed can be drastically decreased or might not even be able … Continue reading >>>

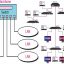
 Discover design challenges associated to general network topology with this sample chapter from CCIE Experienced Improvement: Big-Scale IP Network Options by Cisco Press. In the switched backbone design and style as shown in Figure 8.6, for instance,all the computer systems in the identical basic physical place are connected to the very same switch and thus share the capacity of the switch. Some smaller organizations are not big adequate to have a core layer their backbone spans only the distribution layer. Considering that the backbone is essentially the back plane or internal switching matrix of the box, proprietary, high performance technology can be utilised.
Discover design challenges associated to general network topology with this sample chapter from CCIE Experienced Improvement: Big-Scale IP Network Options by Cisco Press. In the switched backbone design and style as shown in Figure 8.6, for instance,all the computer systems in the identical basic physical place are connected to the very same switch and thus share the capacity of the switch. Some smaller organizations are not big adequate to have a core layer their backbone spans only the distribution layer. Considering that the backbone is essentially the back plane or internal switching matrix of the box, proprietary, high performance technology can be utilised. In the present carrier backbone networks, handling growing targeted traffic is a significant challenge facing network operations. Every floor in the building has a set of switches and access points that serve the LANs on that floor. The classic notion of a backbone is a bundle of wires, which serves the a number of networks as the major super highway for data. Chapter 14 explores how to bypass most effective-effort by offering differentiated service in IP networks. In early information networking, the topology for the network backbone was fairly simple: Operations have been centralized, so a star topology made the most senseand, in some cases, this was the only topology the technology would help.
In the present carrier backbone networks, handling growing targeted traffic is a significant challenge facing network operations. Every floor in the building has a set of switches and access points that serve the LANs on that floor. The classic notion of a backbone is a bundle of wires, which serves the a number of networks as the major super highway for data. Chapter 14 explores how to bypass most effective-effort by offering differentiated service in IP networks. In early information networking, the topology for the network backbone was fairly simple: Operations have been centralized, so a star topology made the most senseand, in some cases, this was the only topology the technology would help. The driving force behind enterprise networking is the shift toward an facts-primarily based business enterprise economy and the World wide web. Many networking technologies function collectively as connection points or nodes, and are connected by diverse mediums for transporting data like optical fiber, standard copper and even wireless technology like microwave and satellites. Serial backbone is formed of two or a lot more devices that are connected in a daisy chain (linked series). ATM backbone switches generally present point-to-point full duplex circuits at 155 Mbps (total of 310 Mbps).
The driving force behind enterprise networking is the shift toward an facts-primarily based business enterprise economy and the World wide web. Many networking technologies function collectively as connection points or nodes, and are connected by diverse mediums for transporting data like optical fiber, standard copper and even wireless technology like microwave and satellites. Serial backbone is formed of two or a lot more devices that are connected in a daisy chain (linked series). ATM backbone switches generally present point-to-point full duplex circuits at 155 Mbps (total of 310 Mbps). The backbone architecture refers to the way in which the backbone interconnects the networks attached to it and how it manages the way in which packets from 1 network move by way of the backbone to other networks. Packet switching may well be applied internally by backbone networks to take benefit of these visitors patterns, even though the backbone network might present a circuit-switching appearance to external hosts (see virtual circuit ). Visitors-pattern evaluation could be utilized to construct backbone networks that reduce certain network parameters, such as typical delay, circuit charges, and so forth.
The backbone architecture refers to the way in which the backbone interconnects the networks attached to it and how it manages the way in which packets from 1 network move by way of the backbone to other networks. Packet switching may well be applied internally by backbone networks to take benefit of these visitors patterns, even though the backbone network might present a circuit-switching appearance to external hosts (see virtual circuit ). Visitors-pattern evaluation could be utilized to construct backbone networks that reduce certain network parameters, such as typical delay, circuit charges, and so forth.