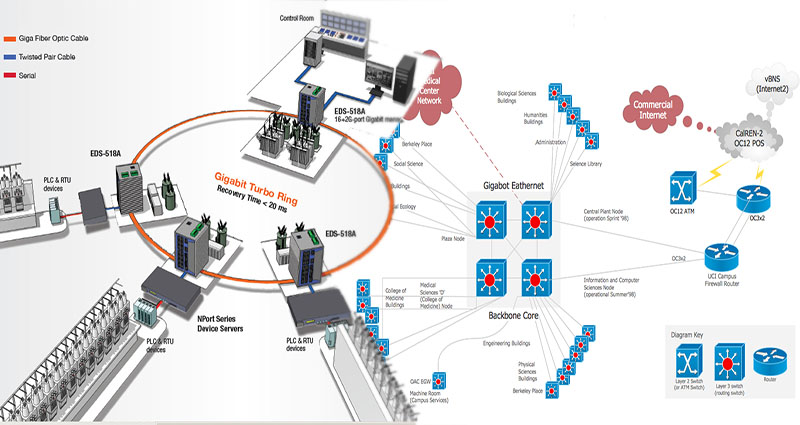
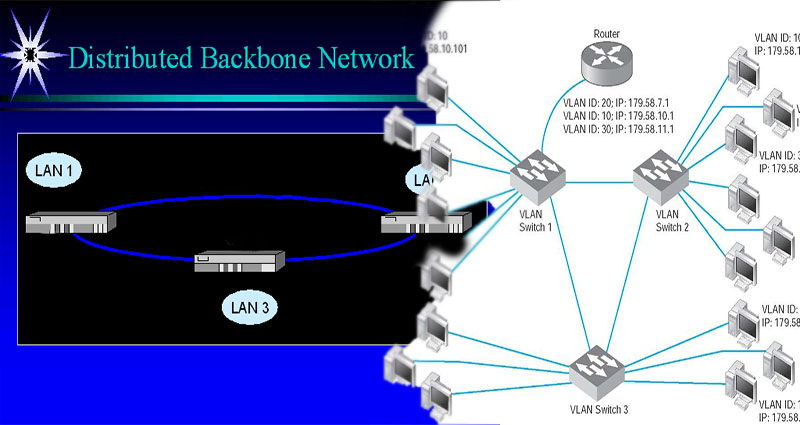
A Backbone Network Example Explained
You have probably heard of Backbone LAN. If not, you may have heard of MPLS and Ethernet. And perhaps you have heard of fiber-optic cabling. In this article, we will review some of the concepts involved in these technologies and give an example of how they work. Read on for more information! You can also learn more about the importance of backbone LAN and Ethernet. You may be surprised to know that these are not the only networking technologies!
Ethernet
Unlike the Internet, which is essentially a network of computers, Ethernet backbone networks have a single central device. The central device, or ‘backbone,’ manages big traffic. It should be powerful and contain plenty of computational power, because the backbone can fail and take down the entire network. This network type is most useful for interconnecting two different types of subnetworks. It can also be a convenient way to troubleshoot issues.… Continue reading >>>